" The natural glycosides contain the aglycone molecule, which is linked to one or more sugar molecules. They are abundant among vegetables for which they represent a source of sugars storage.
The formation of a glycoside determines a higher bioavailability, hydrophilicity and stability compared to substances with lipophilic characters, such as essential oils, allowing the compartmentalization in the vacuole and translocation in the cytoplasm.
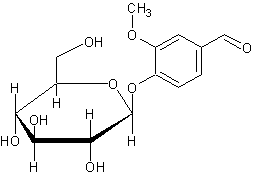
Vanillin β-D-Glucopyranoside (glucovanillin) is a glycoside used as a flavouring agent. In the picture, it is shown the distinctive O-glycosidic bond on carbon 1 of sugar.
WHY GLYCOSIDES?
If we think about the future approach to prevention and early treatment of all diseases and illnesses that afflict humans and animals alike, we believe there are three main reasons to focus our attention on glycosides of vegetable origin:
- Glycosides have a higher bioavailability, hydrophilicity and stability than the corresponding aglycones, in which they can turn into once they have been introduced into the organism or while undergoing simple enzymatic reactions.
- Unlike aglycones, glycosides cannot be easily synthesized, and this guarantees a natural and genuine product, whereas aglycones can be created in a synthetic way and easily sold as natural products.
- They have a unique pharmacological characteristic: the beneficial effects of extracts and infusions of medical herbs are often due to glycosylated molecules.
SOME EXAMPLES
– The glucovanillin is the natural flavour of the common vanilla. Its aglycone, known as vanillin, can be easily created synthetically at low cost, but this is not a product of nature!
– The salicin is a molecule contained in some vegetables that has a high antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and anti-rheumatic characteristic. Unlike the synthetic acetylsalicylic acid (commonly known as aspirin), the salicin doesn’t have any side effect to the stomach even if taken in doses of 300-500 mg.
– Bergamot juice has a cholesterol-lowering effect due to two molecules which have the same effects of statins (medicines with cholesterol-lowering effect) and which are glycosylated.
– There is a type of glycosylated molecules called anthocyanin, which is abundant in nature (black grapes, cherries, strawberries, blueberries, blackberries, blackcurrant, etc.) and which has preventive and curative characteristics against many inflammatory, cardiac, metabolic, neurological, eye diseases and more.
– The echinacoside is the glycoside responsibles of the antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, neurosedative and immunostimulant / adaptogen effects in echinacea estracts.
And there are thousands more examples that can be provided (apples, olives, pomegranates, citrus, beetroot, cabbage/broccoli, mustard, onions, etc.)